Pagination
Pagination is the process of dividing content into separate, discrete pages, making it easier to navigate and consume large amounts of information.
The navigation arrows and limit settings block are removed if the number of records is less than the limit.
This function is available:
Pagination modes:
- Default (nextAndPreviousWithCount)
- nextAndPreviousWithHasNext
- nextAndPreviousSmart
| API Calls (Frontend to Backend) | nextAndPreviousWithCount | nextAndPreviousWithHasNext | nextAndPreviousSmart |
|---|---|---|---|
| /meta | + | + | + |
| /count | + | + (response is ignored) | + (response is ignored) |
| /data | + | + | + |
Info
Pagination won't function until the page is refreshed after adding records.
Use Cases :
nextAndPreviousWithCount: Ideal for backends that leverage database sources.nextAndPreviousWithHasNext: Designed for microservice-based backends where the presence of the next page can be determined, allowing thehasNextflag to be populated.nextAndPreviousSmart: Suitable for microservice-based backends where it is not possible to determine if there is a next page, and thehasNextflag cannot be populated.
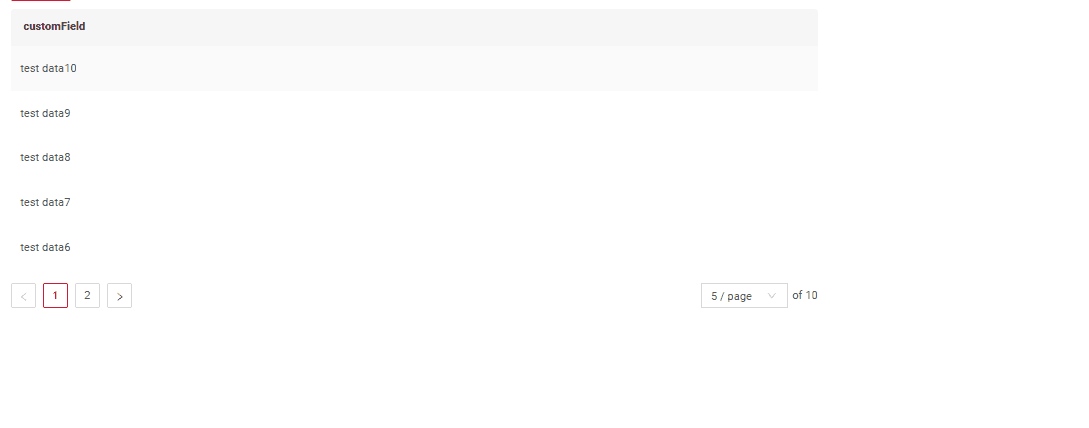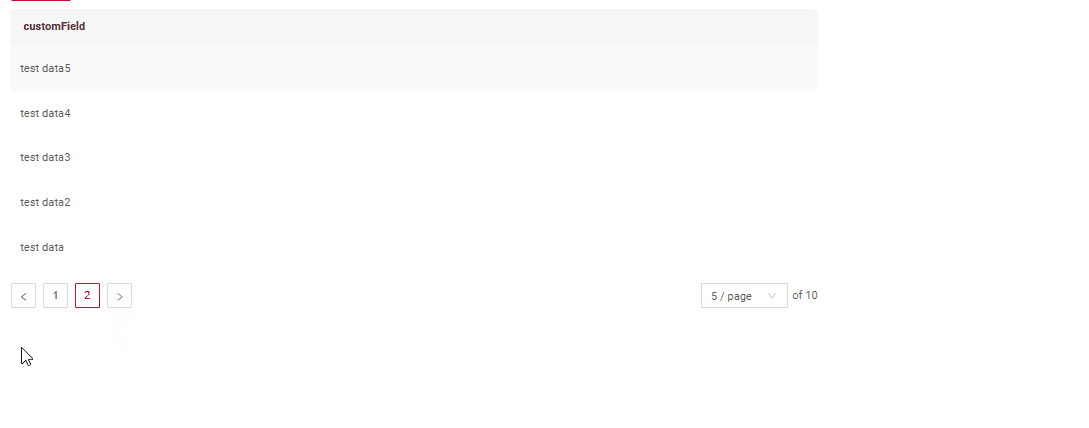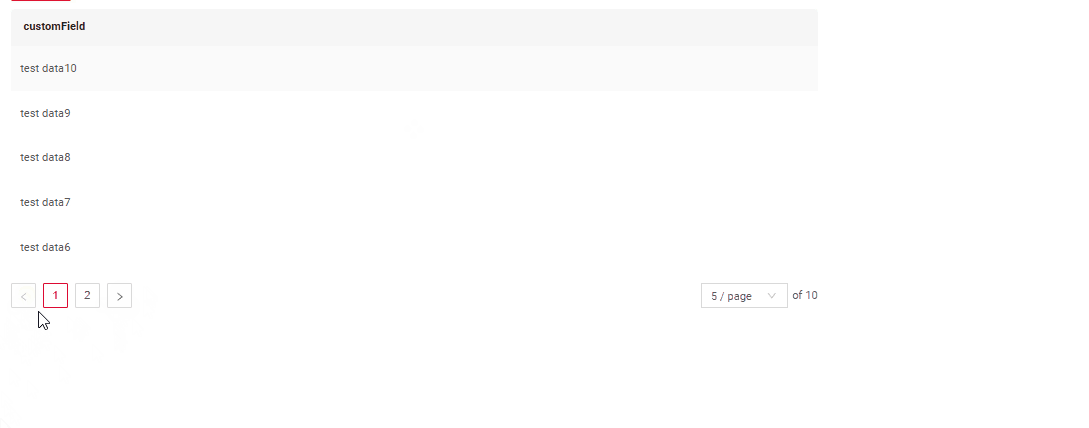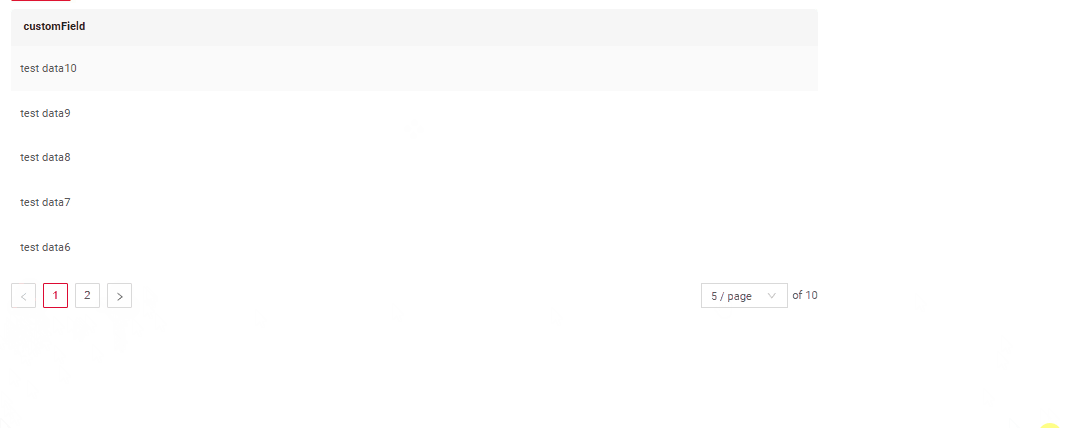
Default (nextAndPreviousWithCount)
Frontend Behavior:
- All three responses are utilized, including the
/countresult. - This mode is best suited for backends that rely on database sources.
How does it look?
How to add?
Example
Option 1. By default
Option 2. Add in options parameter pagination to corresponding .widget.json.
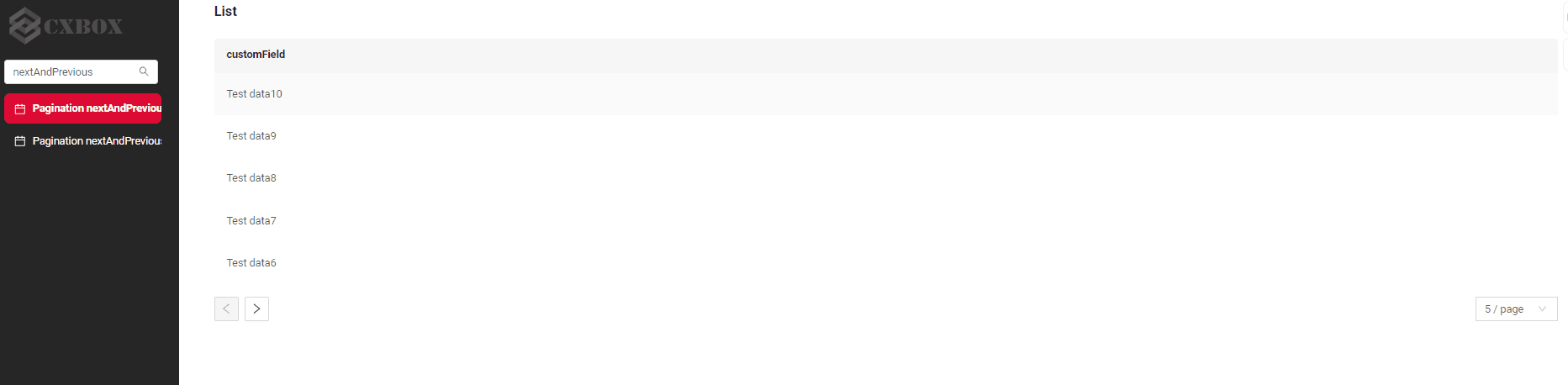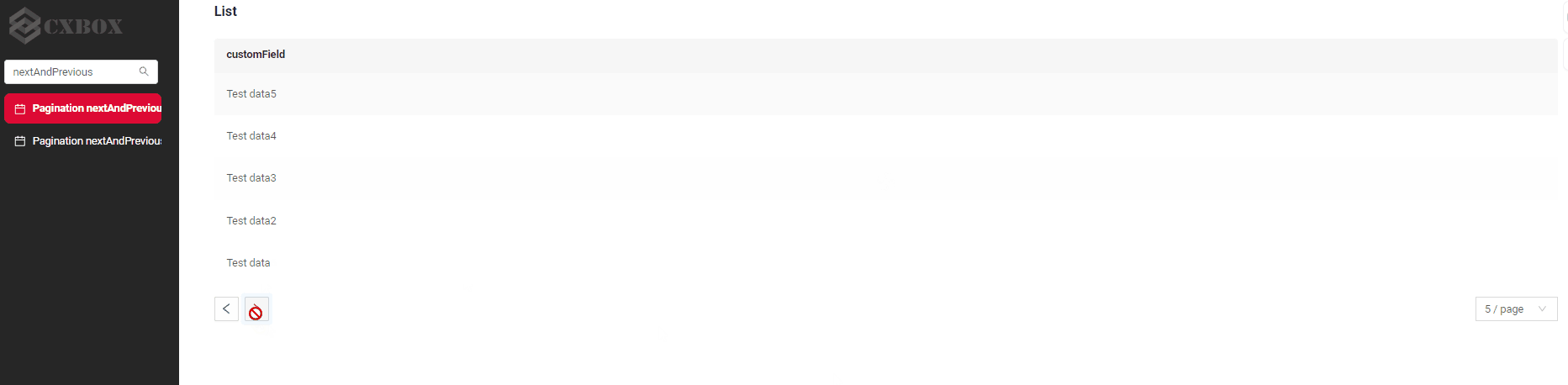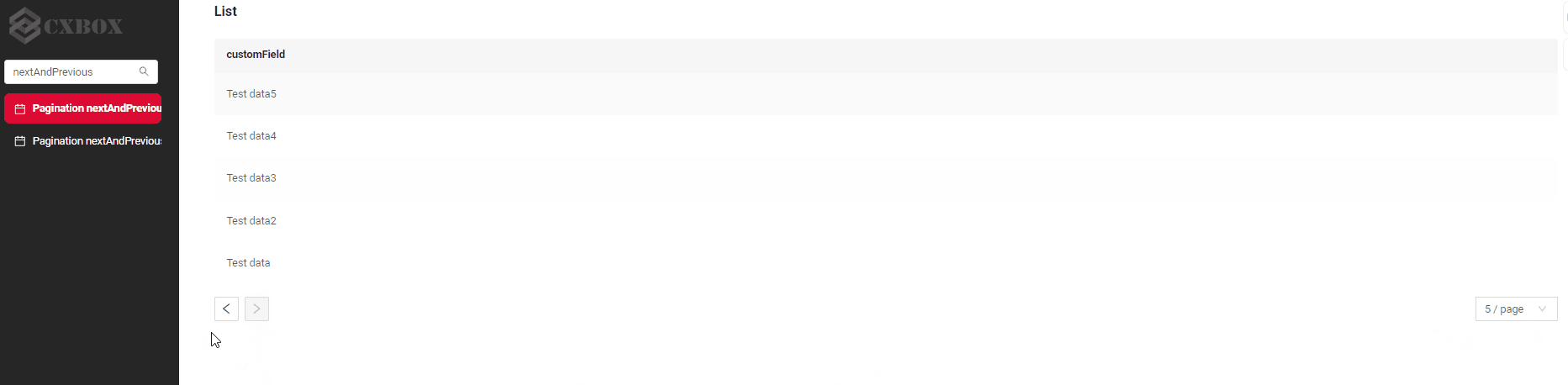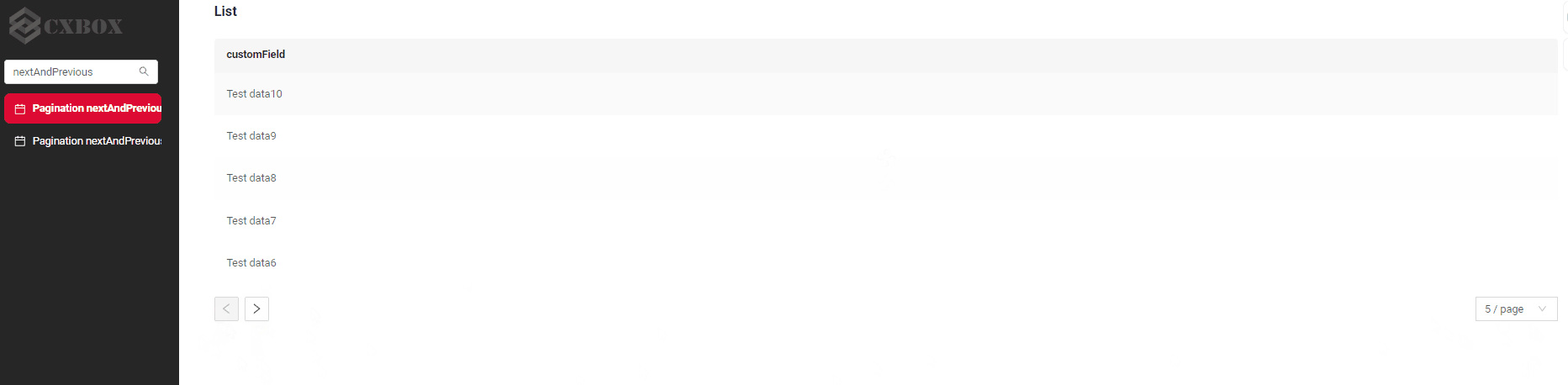
nextAndPreviousWithHasNext
Frontend Behavior:
- The
/countendpoint is called, but its result is not used. - Instead, pagination is based
/datathat indicates whether there is a next or previous page (hasNext/hasPrevious).
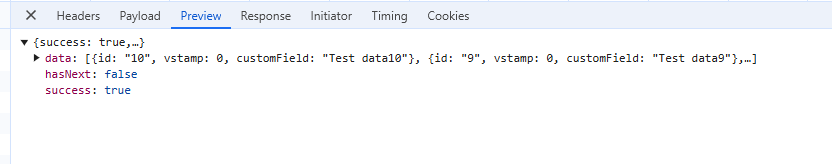
Next button availability logic:
- If hasNext (from /data) is true, Next button is available.
- If hasNext (from /data) is false, Next button is disabled.
How does it look?
How to add?
Example
Add in options parameter pagination to corresponding .widget.json.
{
"name": "MyExampleList",
"title": "Widget property Pagination nextAndPreviousWihHasNext AnySource",
"type": "List",
"bc": "myexample",
"fields": [
{
"title": "customField",
"key": "customField",
"type": "input"
}
],
"options": {
"pagination": {
"type": "nextAndPreviousWihHasNext"
}
}
}
Info
To deactivate the functionality hasNext=trueadd in application.yml cxbox.api.any-source-has-next-enabled = false
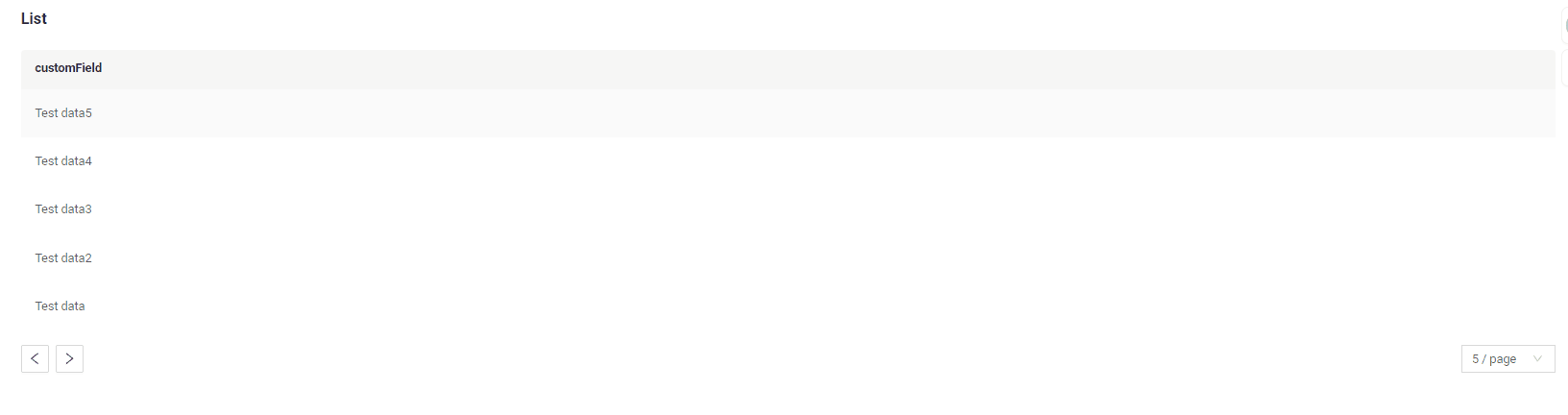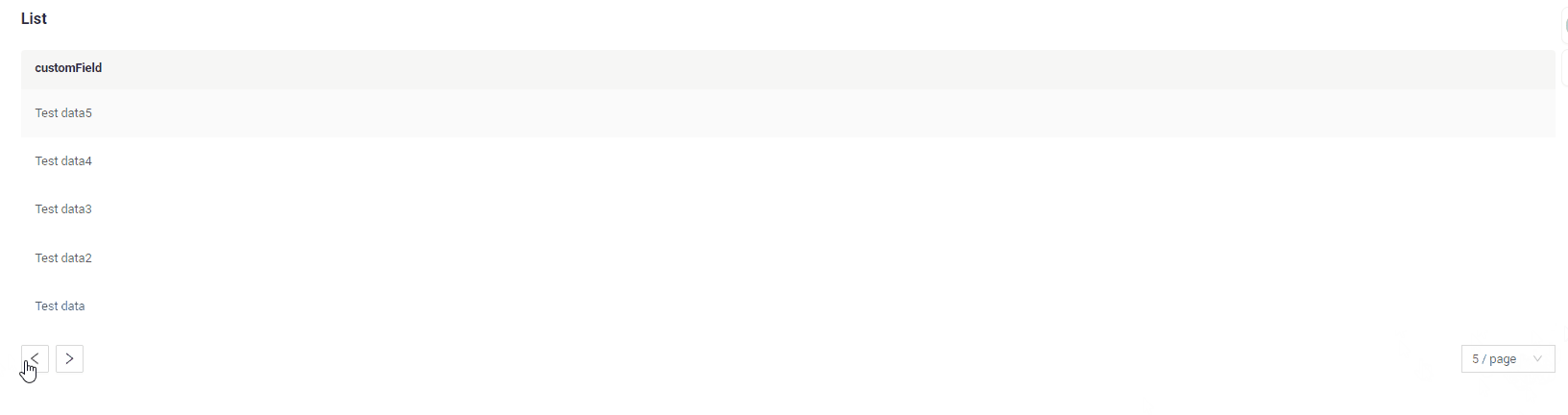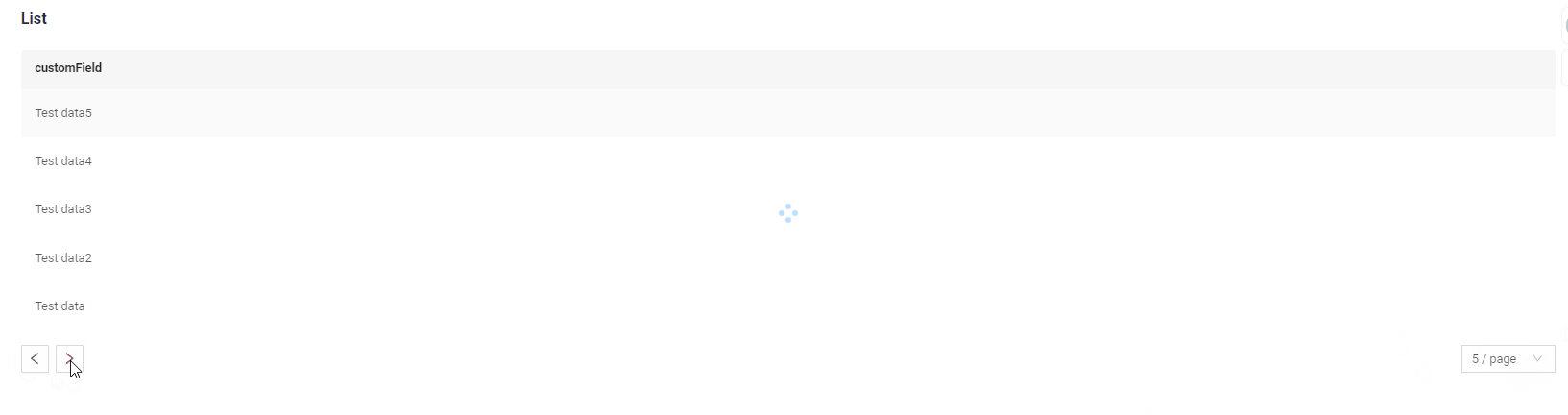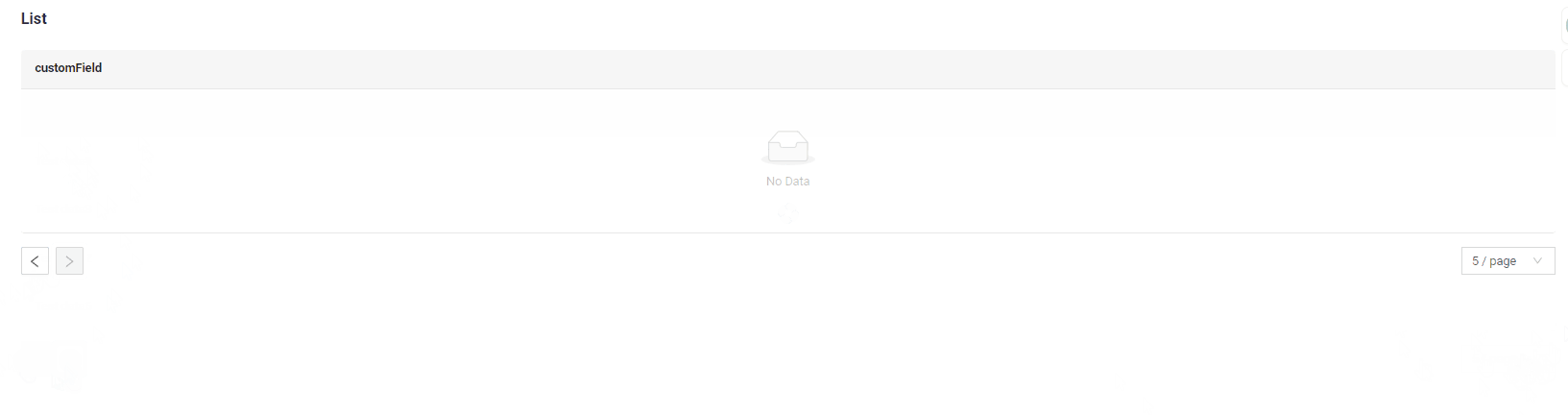
nextAndPreviousSmart
Frontend Behavior:
- The
/countendpoint is called, but its result is not used.
Next button availability logic:
If the number of records received from /data is less than _limit, Next button is disabled.
Disadvantages of this mode:
- If the number of records is a multiple of _limit, a single jump to a page with no records will occur, since it is impossible to determine whether this is the last page.
- If the number of records is a multiple of _limit, a request for the next page will be sent even if it does not exist. If this request returns an error, it should be handled with a try {} catch {} block. (For instance, when retrieving data for the next page from a microservice.)
How does it look?
How to add?
Example
Add in options parameter pagination to corresponding .widget.json.
{
"name": "MyExampleList",
"title": "Widget property Pagination nextAndPreviousSmart AnySource",
"type": "List",
"bc": "myexample",
"fields": [
{
"title": "customField",
"key": "customField",
"type": "input"
}
],
"options": {
"pagination": {
"type": "nextAndPreviousSmart"
}
}
}
hideLimitOptions
Controls the visibility of the records-per-page selection option.
This function is available:
Values:
true– Hides the records-per-page selection option.false(default if not specified) – Shows the records-per-page selection option.
How does it look?

How to add?
Example
Add in options parameter pagination to corresponding .widget.json.
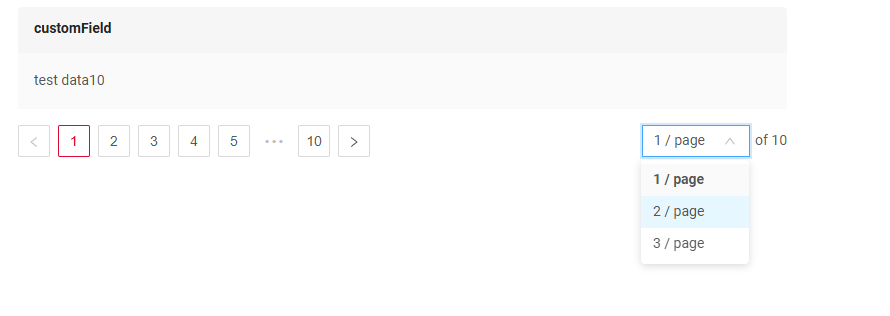
availableLimitsList
Specifies the available options for the number of items displayed per page. Users will see these values in a dropdown.
This function is available:
Values:
An array of integers.
Behavior:
If not provided, the component use default values [5, 10,15, 20].
The user will only be able to select from the specified values.
Use Case:
Restrict pagination options to specific values (e.g., 10, 25, 50, or 100 items per page).
How does it look?
How to add?
Example
Add in options parameter pagination to corresponding .widget.json.